This guide shows how to install, configure, and maintain a terminal server farm based on the Remote Desktop Services (RDS) role on Windows Server. The article will help you to deploy Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2022, 2019, or 2016 in an Active Directory domain.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Components Architecture
The RDS role in Windows Server includes the following components:
- Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) – RDS session hosts. These are the main workhorses of an RDS farm on which user apps run;
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RDCB) – an RDS connection broker. It is used to manage an RDS farm, distribute the workload, reconnect users to their sessions, store RDS collection settings, and published RemoteApps;
- Remote Desktop Gateway (RDGW) – provides secure access to the RDS farm from the Internet;
- RD Web Access (RDWA) – a web interface to access remote desktops and RemoteApps;
- Remote Desktop Licensing (RD Licensing) — a licensing service for managing RDS licenses (CALs).
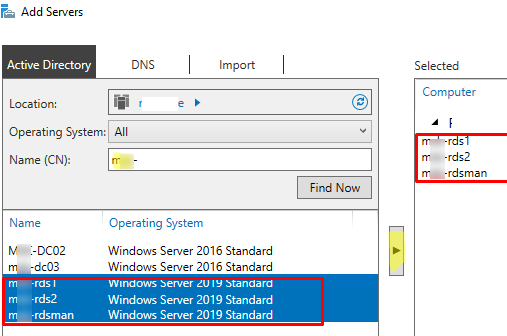
In our small RDS deployment, there are only three Windows Server hosts with the following roles:
mun-rds1.woshub.com— RDSHmun-rds2.woshub.com– RDSHmun-rdsman.woshub.com– RDSH, RDWA, RDCB, and RD Licensing
Prerequisites to create an RDS farm:
- Install the same version of Windows Server on all RDS hosts, configure them, and join the AD domain;
- Open the ADUC console (dsa.msc) and move all hosts with the RDSH role to the same Active Directory OU (Organizational Unit). Thus, it will be easier to apply RDS settings using GPO;
- Create an Active Directory domain security group for RDSH servers (for example, mun-rdsh) and add all hosts to it;
- If you want to use User Profile Disks (UPD) to store RDS user profiles (or roaming profiles), you must create a shared network folder on a file server (it is recommended to place the shared folder on a File Server Failover Cluster running Windows Serveer). Grant Full Control permissions on the shared folder for the mun-rdsh group.
Creating a New RDS Deployment on Windows Server
Let’s see how to create and configure an RDS configuration using the Server Manager GUI.
Open the Server Manager and add all RDS servers you want to the console. Click All Servers -> Add servers.
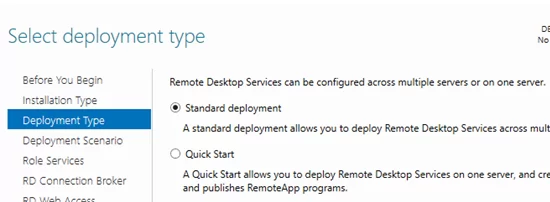
Click the Server Manager menu and select Add Roles and Features -> Remote Desktop Services installation -> Standard deployment –> Session-based deployment.
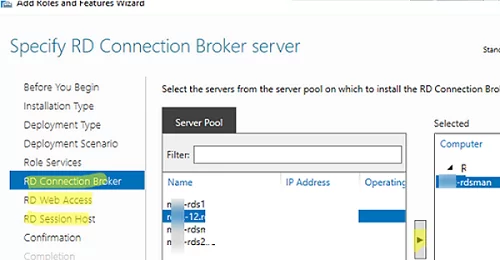
Then specify which RDS roles you want to assign to your hosts. Select the servers for the corresponding roles in the RDS farm creation wizard. In my case, I want to build the following RDS configuration:
- RD Connection Broker –
mun-rdsman - RD Web Access —
mun-rdsman - RD Session hosts —
mun-rdsman,mun-rds1,mun-rds2
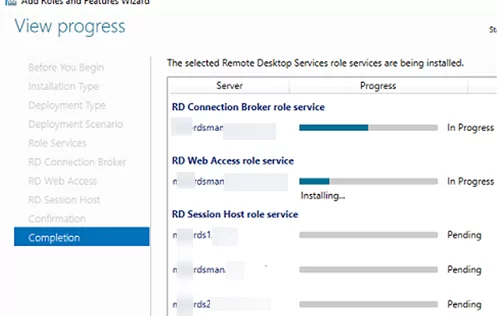
Check Restart destination server automatically if required and click Deploy. Wait until the RDS roles are installed on all servers.
So, your RDS farm is created.
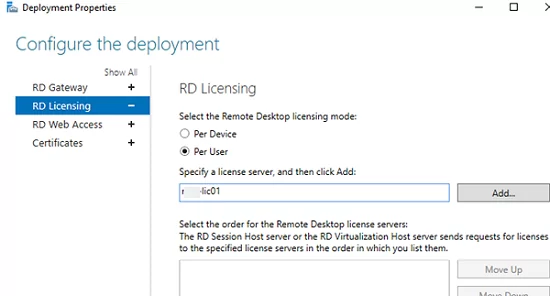
The next step is to install and configure the RDS licensing server. You can install the RD Licensing role on one of the servers on your farm or use an existing RDS licensing server in your domain. Check the detailed guide on how to install, configure and activate the RD Licensing role.
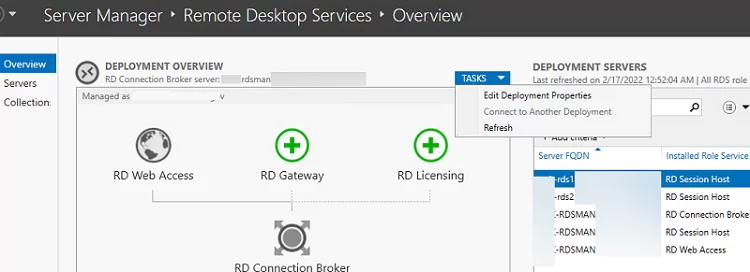
To manage your RDS deployment, open Server Manager -> Remote Desktop Services. The current RDS farm configuration is displayed on the Overview tab.
To change the RDS farm settings, select Tasks -> Edit Deployment Properties in the Deployment Overview section.
Here you can change:
- RD Gateway settings;
- Licensing server address and RDS CAL type (per user/per device);
- View RD Web Access URL;
- Add SSL certificates for RDS (we will skip this step it in the guide).
To build a fault-tolerant Remote Desktop Services farm, you have to provide high availability for the RD Connection Broker role. This is achieved by running multiple RDCB instances (Active/Active) on different servers with a shared SQL Server database that stores the connection broker configuration. You can use the SQL Server Always On high-availability group to make the RDCB SQL database high available. Earlier we published a detailed guide on how to configure a highly available RDS Connection Broker.
Create Remote Desktop Services Collections on Windows Server
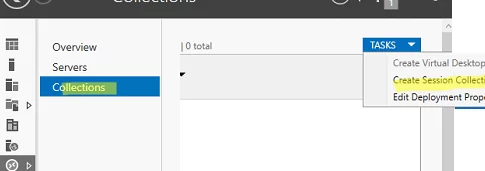
The next step is to create collections of RDS sessions. Remote Desktop collections allow to split hosts in an RDS farm into separate groups or create different sets of settings and available Remote Apps for different groups of users.
Go to Collections and select Edit -> Create Session Collection.
Here you need to:
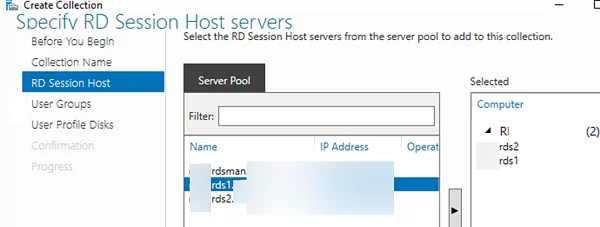
- Specify an RDS collection name:
rds-Mun-Managers; - Select which RDS hosts will serve collection users (one RDSH server may belong to one collection, it is not recommended to have hosts with different Windows Server versions in the same collection);
- In the User Groups tab, specify the groups of users allowed to connect to the collection. Remove the Domain users from the groups and add your group (
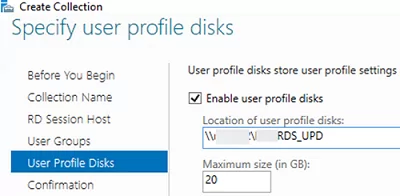
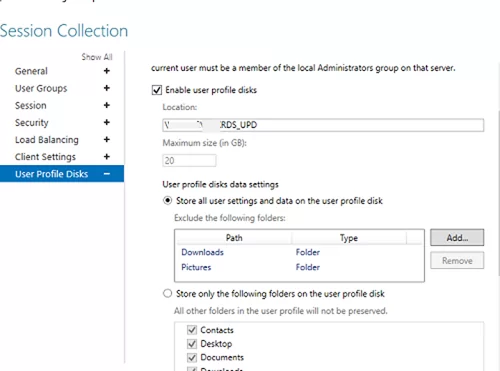
mun-Managers); - On the User Profile Disk tab, check Enable user profile disks if you want to use the UPD vhdx file format to store user profiles. In the Location of user profile disks field, specify the UNC path to your shared folder (for example,
\\mun-fs01\munrds_upd), in which user profile files in the UPD format will be stored and the maximum size of the disk (20 GB by default). When using UPD, if a user logs on to any RDS collection host, the user’s shared profile will always be loaded;Learn more about User Profile Disks in Windows Server RDS in this article. - Click Create to create a new RDS collection;
- Make sure that the UPD file (UVHD-template.vhdx) with the user profile template is created in the specified directory.
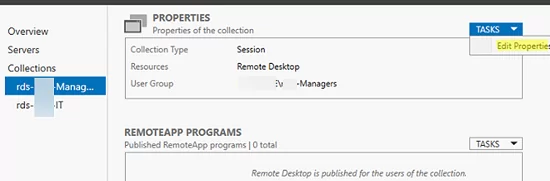
To configure RDS collection settings, select the collection and click Tasks -> Edit Properties.
Here you can change basic collection options (name, description, access groups), and some other settings.
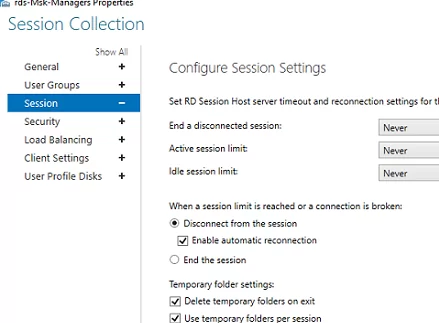
On the Session tab, you may configure reconnection/automatic disconnection options for inactive (idle) RDP sessions (learn more How to Configure Timeouts for RDP Sessions).
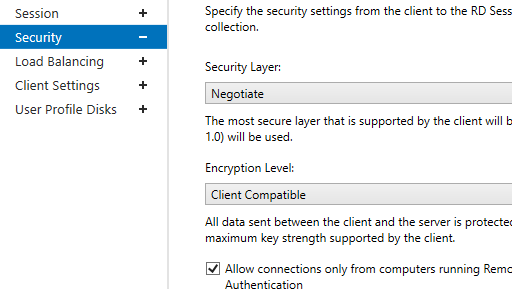
In the Security tab, you may select security (Negotiate, RDP Security level, or SSL/TLS) and encryption (Low, High, Client compatible, or FIPS compliant) settings for RDP sessions. Here you can enable/disable Network Level Authentication (NLA) for RDP.
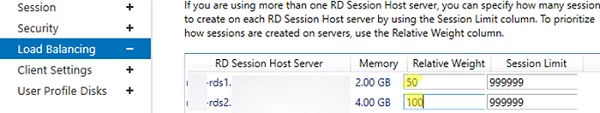
In the Load Balancing tab, you may change RDS host Relative Weight in your farm. If server characteristics (RAM, CPU) in a collection are very different, you need to set a lower weight for the hosts with lower performance. After that, RDCB will distribute user sessions among RDS hosts depending on their weight.
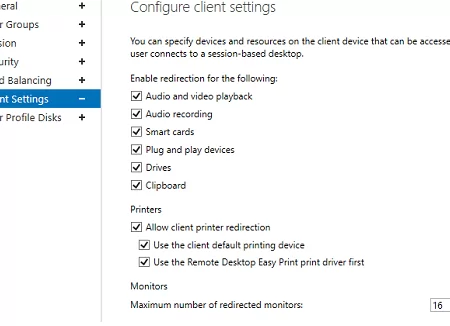
The Client Settings tab allows you to specify which local devices users are allowed to redirect to their RDP sessions. For example, you may enable or disable the redirection of printers, drives, audio devices, or the clipboard from a local user computer to the RDS session.
In the User Profile Disks tab, you may fine-tune UPD settings. You may exclude certain folders or files from sync. It allows to reduce the UPD profile size in a shared network folder and makes a profile load faster (remember that it is loaded over the network from the shared folder when a user logs on).
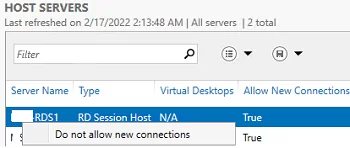
Resize-VHD, which is used to resize Hyper-V virtual VHDX disks.You can put any RDSH server into maintenance mode (RDS Drain Mode) through the HOST SERVERS section of the RDS collection. To do it, click a server and select Do not allow new connection. Then the Connection Broker will not send new user sessions to the RD host. In this mode, you can install Windows updates or update apps on the server without affecting the users.
Here you can also add/remove an RDS host from a collection.
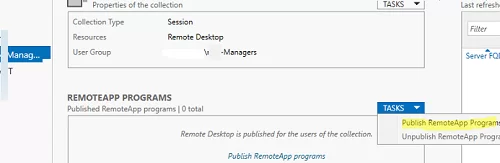
How to Publish RemoteApps in Remote Desktop Services?
RemoteApps are programs published for users on RDS servers. Thanks to RemoteApps, you may use apps installed on a terminal RDSH server as if they are running on a local user computer. The user doesn’t see the entire Windows Server RDS desktop and works only with those apps an administrator has published for them. Only the window of the program running on RDS will be displayed on the user’s computer.
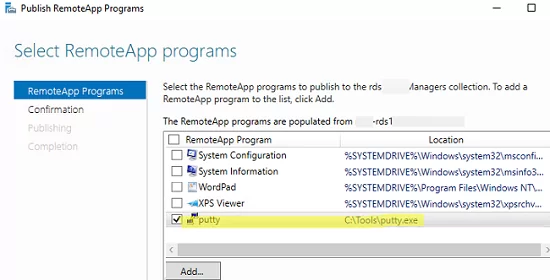
RemoteApps are created in the RDS collection settings. Select Tasks -> Publish RemoteApp Programs in the REMOTEAPP PROGRAMS section.
Windows will list all apps installed on the current RD host. You may select one of them. If there is no app you need in the list, but it is installed on other RDS hosts, click Add and specify the full path to the application’s executable (exe, bat, cmd, etc.).
Publish the RemoteApp.
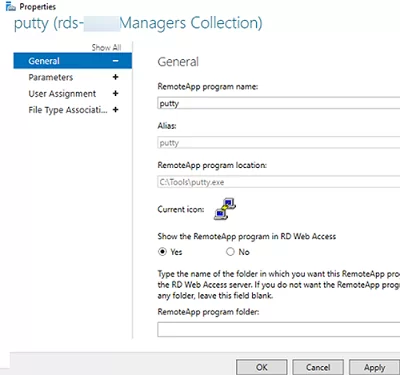
Then you can specify additional app options in the RemoteApp settings.
- Whether you want to show a published RemoteApp in the RD Web Access web interface;
- Set startup options (arguments) for the app (Command-line Parameters -> Always use the following command-line parameters);
- On the User Assignment tab, you can also set restrictions on whether a user or group may run the app.
If you want to change an icon of the published RemoteApp, open the following folder on the server with the RDS Connection Broker role:
C:\Windows\RemotePackages\CPubFarms\rds-Mun-Managers\CPubRemoteApps
Replace the app icon with another ICO file.
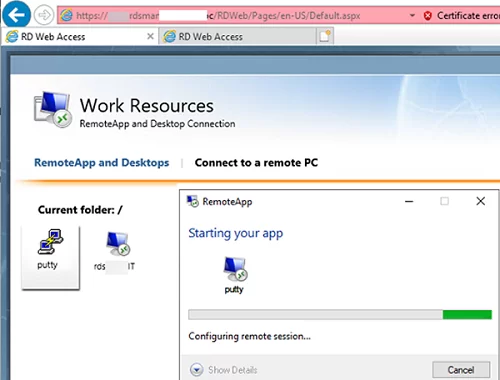
Then a user can run a RemoteApp program from RD Web Access (https://mun-rdsman.woshub.com/RDWeb) or using a special *.RDP file.
To run a published RemoteApp program, you need to add the following lines to the RDP file:
remoteapplicationmode:i:1 remoteapplicationname:s:putty remoteapplicationprogram:s:"C:\Tools\putty.exe" disableremoteappcapscheck:i:1 alternate shell:s:rdpinit.exe
Some useful tips to use your RDS farm conveniently:
- You can configure HTML5 support for the RDWeb Access role. It allows users to connect to RDS servers using any browser or OS even without an RDP client;
- On the RD Web Access server, you can publish a link to change an expired user password (by default, if NLA is enabled you won’t be able to authenticate on an RDSH with an expired Active Directory user password);
- A user guide on how to change a password in an RDP session;
- An administrator can use RD Session Shadow connections to connect/view the desktop of a user session on an RDS server;
- To quickly find which RDS servers have sessions of a specific user, you can use PowerShell:
Import-Module RemoteDesktop
Get-RDUserSession -ConnectionBroker mun-rdsman.woshub.com | where {$_.UserName -eq "a.muller"} | Select HostServer - You can use PowerShell scripts to view RDP connection logs;
- To provide additional security, you can enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for users on your Windows RDS hosts using third-party tools.
How to Deploy Remote Desktop Services Farm Using PowerShell?
If you clearly see the structure of an RDS farm, you can quickly deploy your RDS configuration using PowerShell.
Set the server names in your RDS farm. In this example, I will install the RDCB and RDS licensing roles on separate servers (later it is recommended to enable a highly available RDCB configuration).
$RDSH1 = "mun-rds1.woshub.com"
$RDSH2 = "mun-rds2.woshub.com"
$RDSCB = "mun-rdcb.woshub.com"
$RDSGW = "mun-rdsgw.woshub.com"
Import-Module RemoteDesktop
Install RDS roles on the servers:
Add-WindowsFeature –ComputerName $RDSH1, $RDSH2 -Name RDS-RD-Server –IncludeManagementTools
Add-WindowsFeature –ComputerName $RDSCB -Name RDS-Connection-Broker -IncludeManagementTools
Add-WindowsFeature –ComputerName $RDSGW -Name RDS-Web-Access, RDS-Gateway –IncludeManagementTools
Restart all hosts:
Restart-Computer -ComputerName $RDSH1,$RDSH2,$RDSCB,$RDSGW
Create a new RDSessionDeployment instance:
New-RDSessionDeployment -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB -SessionHost $RDSH1,$RDSH2 –Verbose
Add RDWA and RDGW servers to your farm:
Add-RDServer -Server $RDSGW -Role RDS-WEB-ACCESS -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB
Add-RDServer -Server $RDSGW -Role RDS-GATEWAY -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB -GatewayExternalFqdn "rds.woshub.com"
You can list the RDS roles and hostnames in your farm:
Get-RDServer -ConnectionBroker $RDSGW
Install the RDS Licensing role using the Add-WindowsFeatures cmdlet:
Add-WindowsFeature –ComputerName $RDSCB -Name RDS-Licensing, RDS-Licensing-UI
Set a PerUser RDS licensing mode:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $RDSCB -ScriptBlock {Set-RDLicenseConfiguration -Mode PerUser -LicenseServer $RDSCB -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB}
Add-RDServer -Server $RDSCB -Role RDS-LICENSING -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB
Add a licensing server to a domain security group using Add-ADGroupMember:
Add-ADGroupMember "Terminal Server License Servers" -Members "mun-rdcb$"
If you have a certificate for the RDS, you can add it to your farm configuration (you may use the free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate for your RDS host):
$Path = "C:\ps\RDSCert.pfx"
$Password = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "setCertificPAssw00rd11-" -AsPlainText -Force
Set-RDCertificate -Role RDGateway -ImportPath $Path -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB -Force
Set-RDCertificate -Role RDWebAccess -ImportPath $Path -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB -Force
Set-RDCertificate -Role RDPublishing -ImportPath $Path -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB -Force
Set-RDCertificate -Role RDRedirector -ImportPath $Path -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB -Force
To get information about the installed SSL certificates:
Get-RDCertificate
Then you can create RDS collections:
$CollectionName = "ITdept"
New-RDSessionCollection –CollectionName $CollectionName –SessionHost $RDSH1,$RDSH2 –ConnectionBroker $RDSCB –CollectionDescription “IT department management collection”
To allow access to RDS servers for groups:
$UserGroup =@("WOSHUB\mun-admins","WOSHUB\mun-devops")
Set-RDSessionCollectionConfiguration -CollectionName $CollectionName -UserGroup $UserGroup
To publish a RemoteApp program:
New-RDRemoteapp -Alias GoogleChrome -DisplayName GoogleChrome -FilePath "C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe" -ShowInWebAccess 1 -CollectionName $CollectionName -ConnectionBroker $RDSCB
In this article, we covered how to install and configure a Remote Desktop Services farm on Windows Server 2019/2022 using the Server Manager graphical interface and PowerShell. The RD Web Access and RD Gateway roles are not described here. We’ll show how to configure these roles in future articles.
10 comments
Hello, usefull article for basics on RDS deployement but usage UPD is highly not recommended since free availability of FSLOGIX !
I plan to describe the specific of using FSLogix profiles in an RDS environment in the upcoming posts.
Stay tuned
https://woshub.com/fslogix-profiles-windows-server-rds/
Thanks for your guide.
everything seems ok but user sessions in farm are not listed.
I couldn’t find a solution. Do you have any suggestions?
You can use the Get-RDUserSession PowerShell cmdlet to get a list of all user sessions in a collection or in a Remote Desktop deployment
Get-RDUserSession -ConnectionBroker “rdcb.woshub.com”
Or do you want to view the list through the RDS GUI?
I have 4 servers in Workgroup. Is it also possible to create this RDS farm without AD/domain?
You can only deploy 4 standalone RDS hosts in a workgroup environment.
https://woshub.com/install-remote-desktop-services-rdsh-workgroup-without-domain/
And you will have to create RDS users on each server manually, which is extremely inconvenient
You can download a configured *.rdp file for your RemoteApp from the RDWeb start page instead of creating it manually.
Do I need to have the apps I want to remotely publish in the broker to be available on both RDS Hosts? In your example, you tell me to publish a remote app I need to point to its’ path, which can be in the broker or one of the other hosts. Does it need to be in both hosts or one is enough and the broker will still divide the connections to to both RDS hosts?
Of course, all the servers in your RDS collection must have the same configuration.